Thin-wall bearing, as the name suggests, is a very thin bearing section. It has a wide range of uses and is indispensable in industrial production. It has the advantages of light weight, compact structure and small moment of inertia. It is widely used in industrial robots, aerospace vehicles, space satellites, medical and other products, and the market size is gradually increasing.
1. Reduce the total cost of the equipment. Thin-walled bearings help reduce the total cost of the equipment. Generally speaking, the total cost decreases significantly with the increase of the inner diameter of the thin-walled bearing, and the savings are 30% to 40% of the material and parts costs.
2. Reduction in volume and weight. As the inner diameter increases, the increase in volume and weight also decreases significantly. For example, if the outer diameter doubles, the weight of the thin-walled bearing only increases by 2.3 times, while the life of the traditional ultra-light 618 series bearing increases by 6 times. 9 times, and the heavier series bearings have a higher weight coefficient. The reduction in the volume and weight of thin-walled bearings also reduces the volume and weight of the entire assembly of the device. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the use of thin-walled bearings in the initial design stage of the entire device.

3. Low-cost hollow shafts can be used. During the determination of the bearing cross-sectional size, the diameter of the rotating shaft can wait until the design stage. This approach often allows the design to adopt a low-cost hollow shaft instead of the usual solid shaft (main column) design. In this way, hydraulic lines, wires and connectors can be arranged in the hollow shaft. These pipes can be better protected and take up less space in the hollow shaft.
4. Allows greater standardization of parts. Another advantage of thin-walled bearings is that it allows a greater degree of part standardization when a series of products with different sizes are produced according to the diameter or power requirements of the rotating shaft. Select a series of thin-walled bearings with the same standard cross-sectional dimensions from the product series to meet the needs of a variety of different rotating shaft diameters with a smaller bearing seat size.
The ratio of the inner diameter to the outer diameter of a thin-walled bearing is less than the specified value. A bearing with a ratio of the outer diameter to the inner diameter below 1.25 is called a thin-walled ball bearing. This means that the value of the outer diameter to the inner diameter of the bearing is very small, and the bearing wall is very thin, so it is called a thin-walled ball bearing.
Thin-wall bearings require high precision. Because the wall is very thin, the load-bearing capacity is also very low and the impact resistance is very poor. It depends on the use environment.Come and choose!
Thin-wall bearings have a simple structure and are easy to use. They are mainly used to bear radial loads, but when the radial clearance of the bearing increases, it has an angular contact ball The bearing has certain performance and can bear radial and axial combined loads. When the speed is high and the thrust ball bearing is not suitable, it can also be used to bear pure axial loads. Compared with other types of bearings of the same size, this bearing has a higher friction The coefficient is small and the speed is high. But it is not impact-resistant and is not suitable for bearing heavy loads.
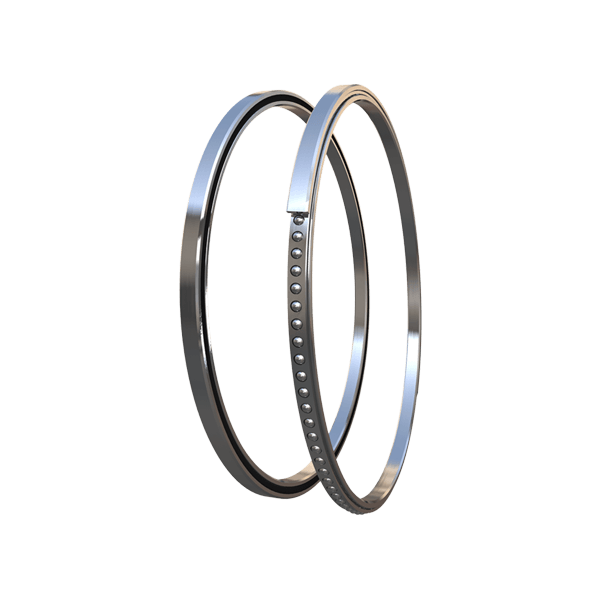 Thin Section Bearings
Thin Section Bearings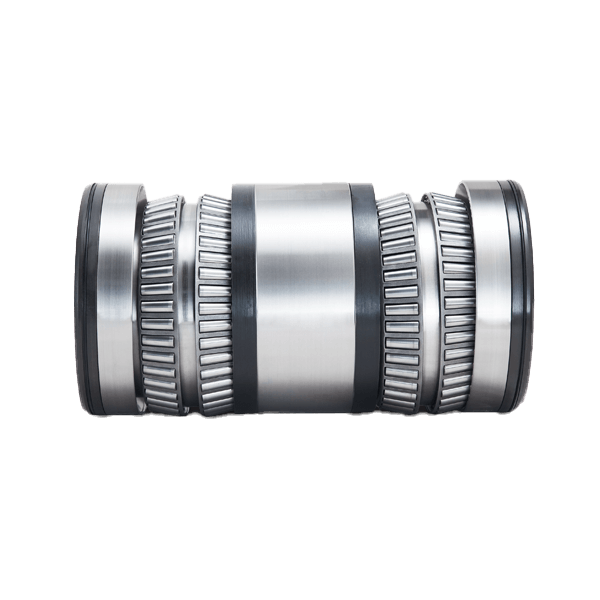 Heavy Duty Bearings
Heavy Duty Bearings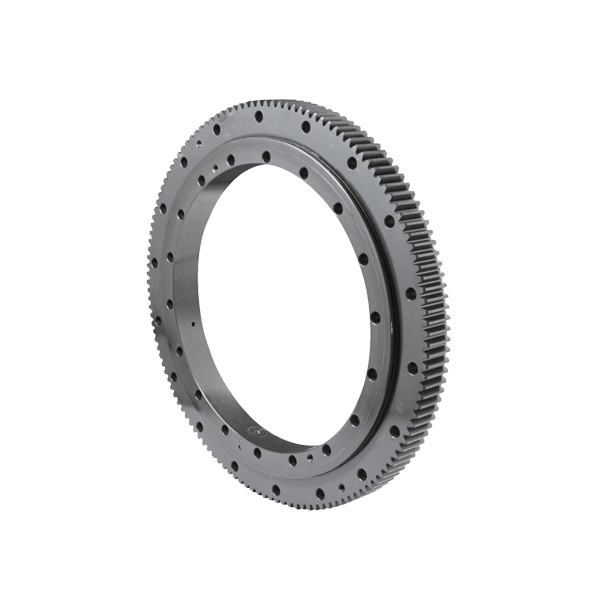 Slewing Bearing
Slewing Bearing Rolling Element
Rolling Element Thin Section Bearings
Thin Section Bearings Heavy Duty Bearings
Heavy Duty Bearings Slewing Bearing
Slewing Bearing Rolling Element
Rolling Element Thin Section Bearings
Thin Section Bearings Heavy Duty Bearings
Heavy Duty Bearings Slewing Bearing
Slewing Bearing Rolling Element
Rolling Element